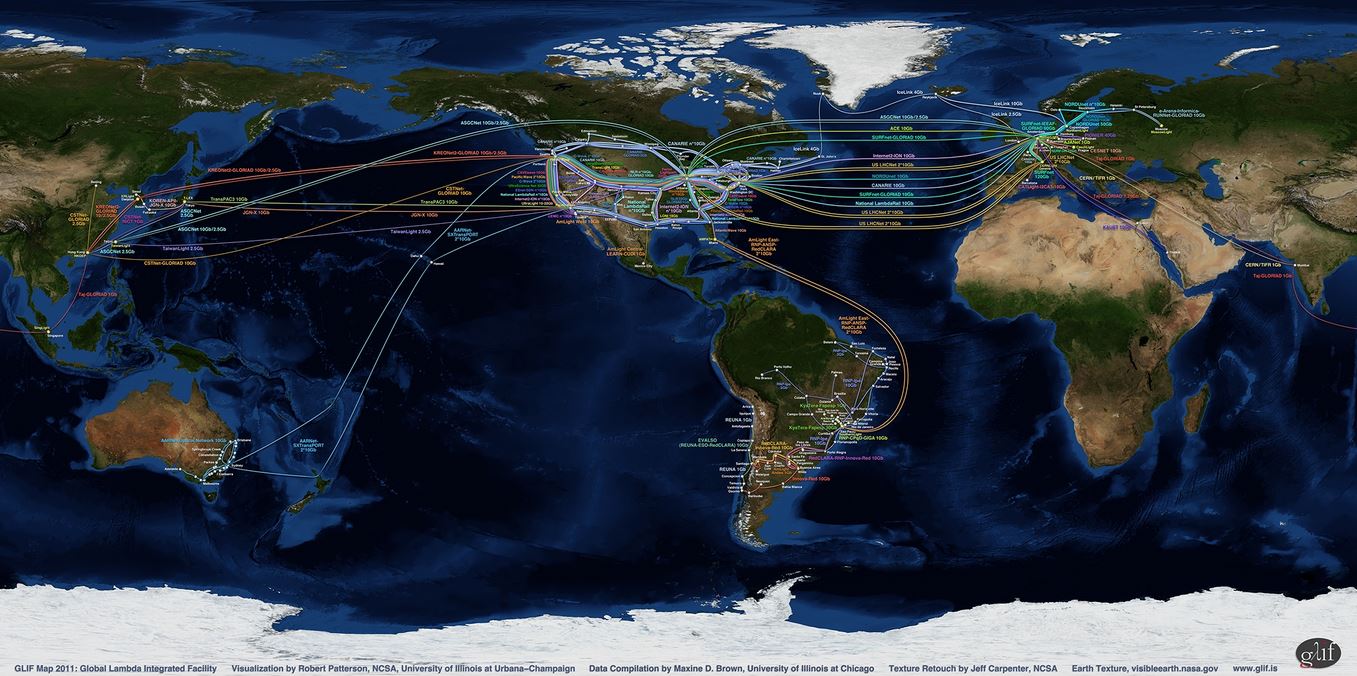
25 May 2011 — GLIF, the Global Lambda Integrated Facility, announces the availability of new world and regional maps that showcase its advanced research and education multi-gigabit optical network infrastructure. The infrastructure has grown since the original map was created in 2005, with participation from more National Research & Education Networks, consortia, institutions and individual research initiatives, in more countries and continents. These participants provide the physical lambda networks that are interconnected at GLIF Open Lightpath Exchanges, or GOLEs. GOLEs have the equipment necessary to interconnect and establish end-to-end lightpaths, which are used by international research teams who are working together to discover innovative solutions to complex problems of global importance.
GLIF is a virtual organization or facility of network providers, network engineers, computer scientists and computational scientists who are developing new computing paradigms and cyberinfrastructure, based on optical networks, to enable international multidisciplinary teams to work together. Science has no geographical boundaries, and GLIF’s network of interconnected optical wavelengths (also known as /lambda grids/) is used to dynamically create powerful distributed systems of computers, data storage, visualization displays and instruments at collaborating sites around the globe, making it easier for researchers to share resources, information and knowledge.
The GLIF map does *not* represent all the world’s Research & Education optical networks. The GLIF map also does not show international capacity that is dedicated to production usage. The GLIF map only illustrates *excess* capacity that its participants are willing to share with international research teams for applications-driven and computer-system experiments. GLIF’s resource providers agree to share all or part of their lambdas, all or some of the time. GLIF does not provide any network services itself and researchers should approach individual GLIF network resource providers to obtain lightpath services.
The GLIF Map 2011 visualization was created by Robert Patterson of the Advanced Visualization Laboratory (AVL) at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC), using an Earth image provided by NASA with texture retouching by Jeff Carpenter, NCSA. Data was compiled by Maxine D. Brown of the Electronic Visualization Laboratory (EVL) at the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC). Support was provided by GLIF, NCSA/UIUC, the State of Illinois, and US National Science Foundation grant # OCI-0962997 to EVL/UIC.
For more information on GLIF, and to download the world and regional maps in a variety of formats and resolutions, click here .
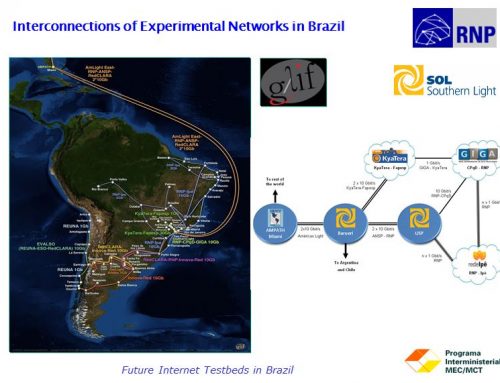
*Participating Networks* — AARNet Optical Network (Australia), AARNet-SXTransPORT (Australia), ACE (US), AJANet (Germany), AmLight Andes (US/South America), AmLight Central-LEARN-CUDI (US/Mexico), AmLight East/RNP-ANSP-RedCLARA (US/South America), AmLight West (US/Mexico), ASGCNet (Taiwan), AtlanticWave (US), C-Wave (US), CANARIE (Canada), CATLight-i2CAT (Catalonia), CAVEwave (US), CENIC (US), CERN-TIFR (Switzerland/India), CESNET (Czech Republic), CSTNet-GLORIAD (China), CSTNet-NICT (China/Japan), e-Arena-Informica-RUNNet-GLORIAD (Russia), ESnet-SDN (US), EVALSO/REUNA-ESO-RedCLARA (South America), Fermi Lightpath (US), Florida LambdaRail (US), IceLink (Nordic Region/Canada/GLORIAD), IllinoisWave (US), Innova-Red (Argentina). Internet2-ION (US), JGN-X (Japan), KAUST (Saudi Arabia), KOREN-APII-JGN-X (South Korea/Japan), KREONet2-GLORIAD (South Korea), KyaTera-Fapesp (Brazil), LONI (US), MiLR-UltraLight (US). National LambdaRail (US), NORDUnet (Nordic Region), Pacific Wave (US), PIONIER (Poland), RedCLARA-Innova-Red (South America), RedCLARA-RNP-Innova-Red (South America), REUNA (Chile), RNP-CPqD-GIGA (Brazil), RNP-Ipe (Brazil), Southern Light Rail (US), SURFnet (Netherlands), TaiwanLight (Taiwan), Taj-GLORIAD (US/Egypt/India/Singapore), Teraflow (US), TransLight (US), TransPAC3 (US), UltraLight (US), UltraScience Net (US), and US LHCNet (US).
*Participating GOLEs* — AMPATH (Miami), CERNLight (Geneva), CzechLight (Prague), HKOEP (Hong Kong), KRLight (Daejoen), MAN LAN (New York), MoscowLight (Moscow), NetherLight (Amsterdam), NGIX-East (Washington DC), NorthernLight (Copenhagen), Pacific Wave (Los Angeles, Seattle, and Sunnyvale), SingLight (Singapore), SouthernLight (São Paulo), StarLight (Chicago), T-LEX (Tokyo), and TaiwanLight (Taipei).